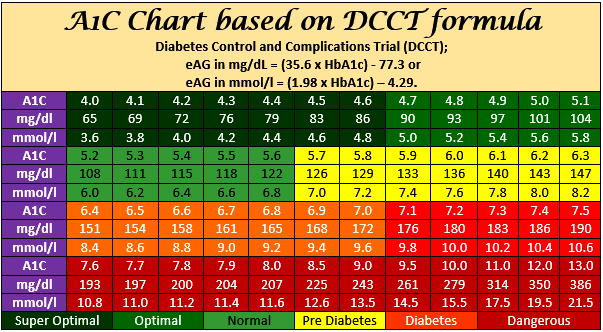
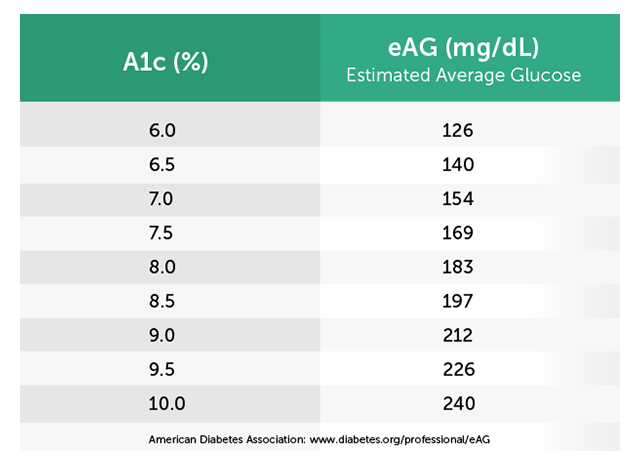
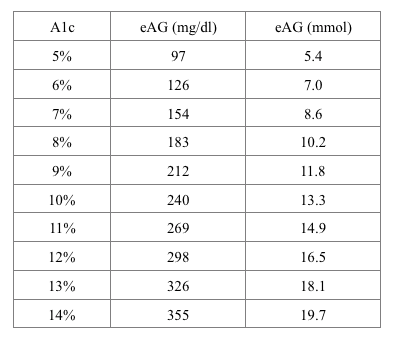
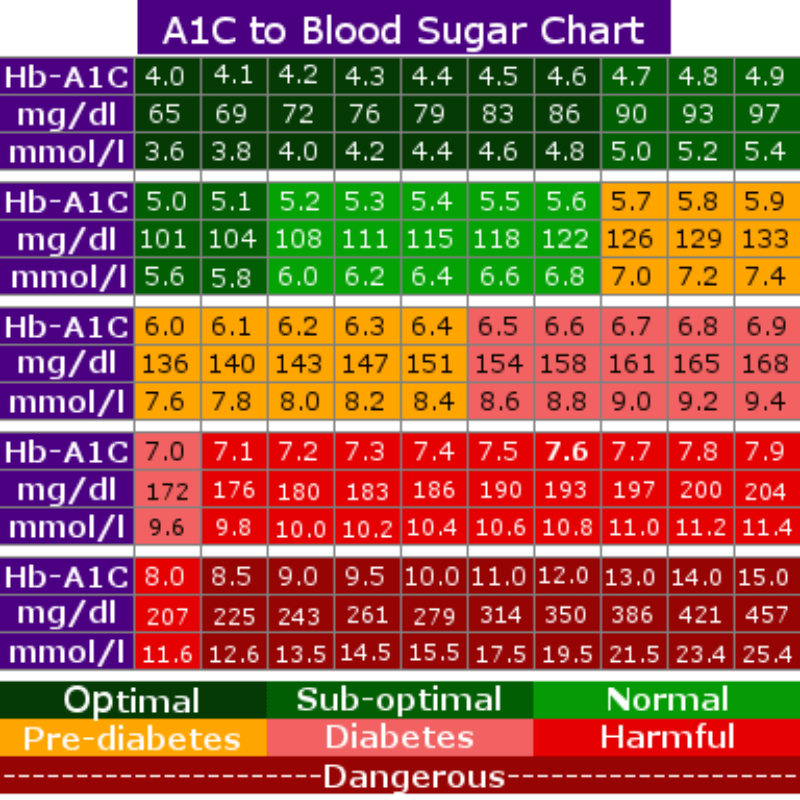
Blood Sugar To A1c

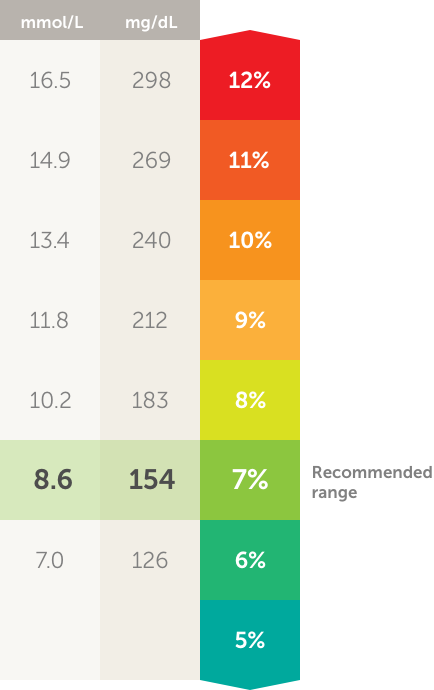
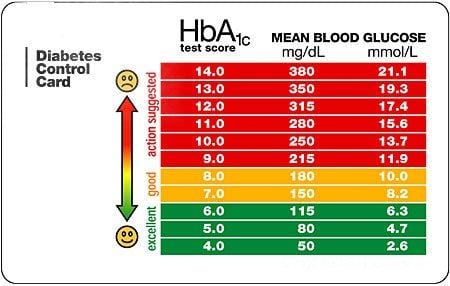
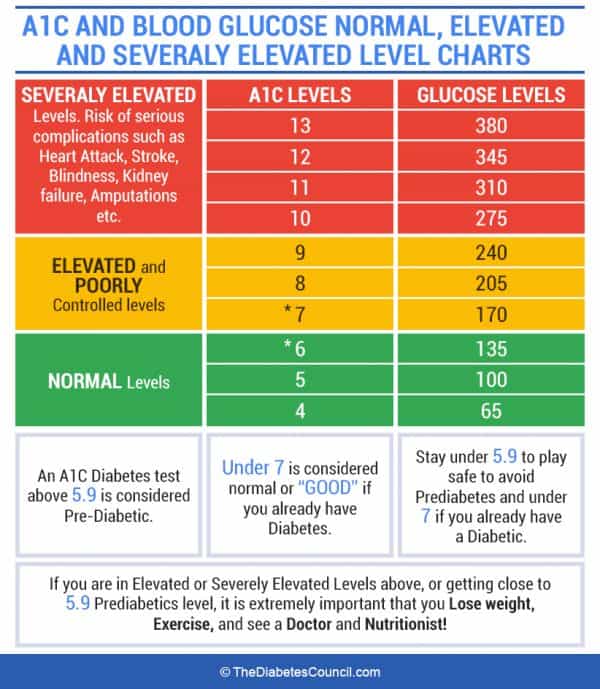
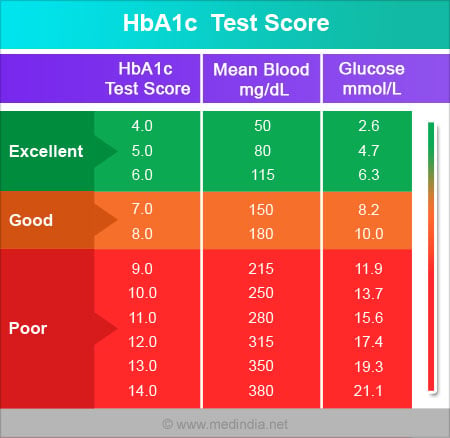
A1c measures blood sugar over the last three months by looking at the percentage of hemoglobin saturated with sugar.
Blood sugar to a1c. The sugar in your blood is called glucose. Hemoglobin is a protein found inside red blood cells that carries oxygen to the body. A1c is an important tool for managing diabetes but it doesnt replace regular blood sugar testing at home. A blood glucose test taken at home measures your current blood glucose measured in milligrams per decilitre or millimoles per litre.
Their lifespan is approximately three months. Your eag is another term rarely used in doctors offices but its pretty darn important if youre trying to improve your a1c. Glucose attaches to or binds with hemoglobin in your blood cells and the a1c test is based on this attachment of glucose to hemoglobin. Hemoglobin cells are constantly dying and regenerating.
Before we start talking about a1c results we need to clear up one thing. Hemoglobin is the part of a red blood cell that carries oxygen to the cells. Some blood sugar or glucose naturally attaches itself to a1c cells as they move through your bloodstream. Your eag is simply your estimated average glucose level or blood sugar level.
A1c measures the amount of hemoglobin in the blood that has glucose attached to it. The higher the glucose level in your bloodstream the more glucose will attach to the hemoglobin. Red blood cells live for about 3 months so the test shows the average level of glucose in your blood for the past 3 months. Blood sugar can be measured in a variety of ways which often leads to confusion.
The a1c test measures how much glucose is bound. Specifically the a1c test measures what percentage of your hemoglobin a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen is coated with sugar glycated. Two people can have the same a1c one with steady blood sugar levels and the other with high and low swings. When glucose builds up in your blood it binds to the hemoglobin in your red blood cells.